Effective Strategies to Manage High Blood Pressure for Long-Term Health
Managing high blood pressure effectively is crucial for protecting your long-term health and preventing serious health issues associated with this common condition. Millions of people globally face this health challenge, often without realising the dangers it poses. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, occurs when blood consistently applies excessive pressure on the arterial walls. This ongoing pressure can cause damage to blood vessels and exert significant stress on the heart. If hypertension is left unchecked, it can develop into severe health issues such as heart disease, stroke, or kidney failure. Understanding your blood pressure readings and recognising the various factors that can lead to increased levels is the first step in managing high blood pressure effectively.
A hereditary tendency may increase your likelihood of developing hypertension. If your family has a history of high blood pressure, you might find yourself at a higher risk of encountering this issue earlier in life. However, lifestyle choices play a significant role in shaping this risk as well. Diets rich in salt, insufficient intake of vegetables, and excessive alcohol consumption can all heighten your chances of developing hypertension. Additionally, a lack of physical activity and weight gain contribute to increasing blood pressure levels. Poor lifestyle choices and modern living have led to a rise in the incidence of hypertension. Nevertheless, with heightened awareness and proactive health measures, individuals can drastically improve their health outcomes.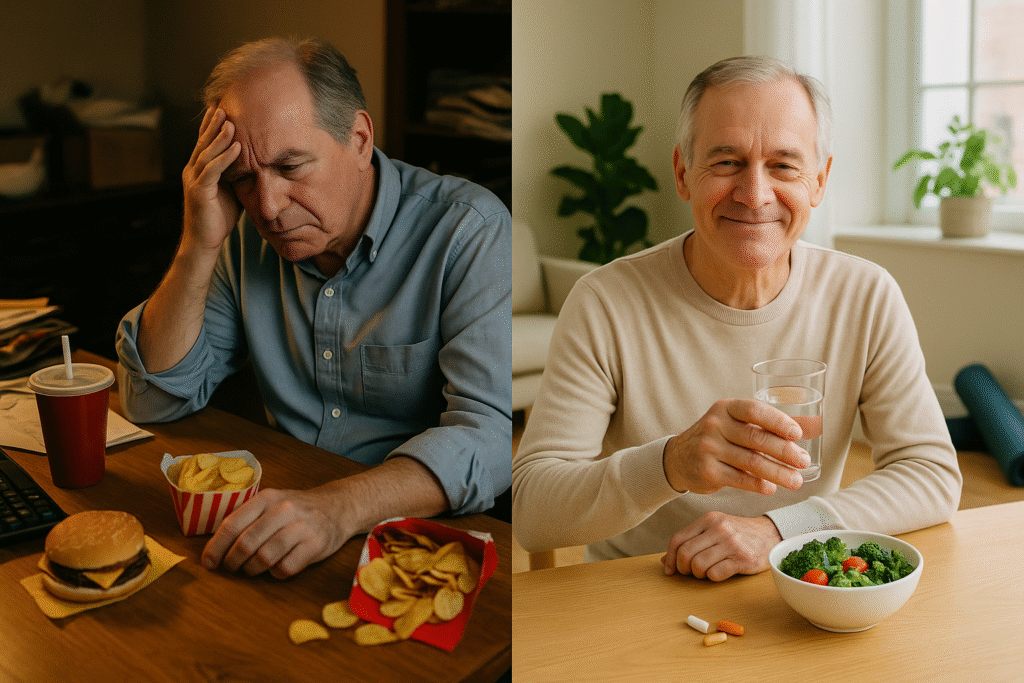
Many individuals who struggle with high blood pressure often do not present any obvious symptoms. This is why hypertension is commonly referred to as the “silent killer.” Relying solely on symptoms to assess your health can lead to incorrect conclusions. Regular monitoring and health assessments are essential to truly understand your blood pressure levels. As readings can vary, routine checks are vital for effective management. If you are diagnosed with hypertension, making simple lifestyle changes can be incredibly beneficial. Increasing your physical activity, choosing healthier foods, and applying effective stress management techniques can significantly reduce your blood pressure and improve your overall well-being. If these lifestyle adjustments are insufficient, consulting a healthcare professional about suitable medication options might be advisable.
Effectively managing high blood pressure requires a comprehensive strategy that includes healthy lifestyle choices, consistent monitoring, and, if necessary, medication. This all-encompassing approach significantly lowers the risk of developing serious health complications. The sooner you take charge of your heart health, the more positive your outcomes will be. By taking an active role in hypertension management, you can improve your quality of life now and in the future.
Raising Awareness About High Blood Pressure: The Importance of Understanding
High blood pressure, medically termed hypertension, signifies that your blood pressure readings consistently fall outside the healthy range. Blood pressure is measured in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) and consists of two numbers: systolic (the pressure during heartbeats) and diastolic (the pressure between beats). A typical reading is around 120/80 mmHg, whereas any readings exceeding 130/80 mmHg usually indicate some level of hypertension.
Hypertension is primarily categorised into two types. Primary hypertension develops gradually and is often influenced by both genetic and lifestyle factors. In contrast, secondary hypertension can result from other medical conditions, such as kidney disease or hormonal imbalances. Both types of hypertension can place significant stress on the heart and arteries, potentially leading to kidney damage and negatively impacting cognitive function. Identifying the specific type of hypertension you are experiencing is essential for appropriate management and treatment.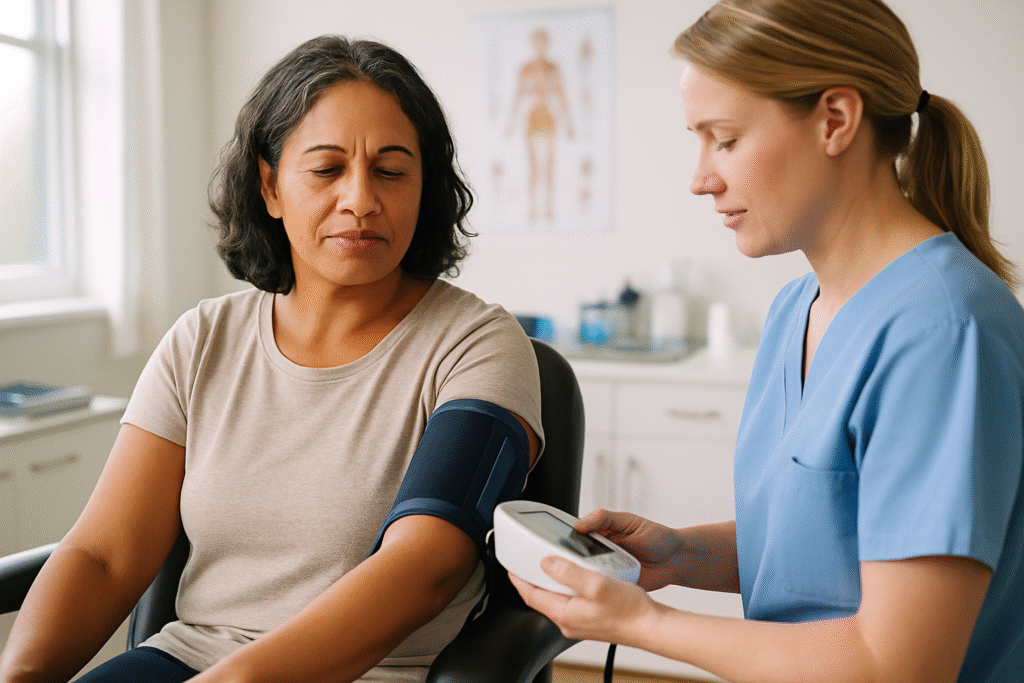
Managing high blood pressure often requires significant adjustments to your daily routine and a close collaboration with healthcare professionals. Many individuals are unaware of their condition since symptoms rarely present themselves. This underscores the necessity of regular health check-ups, as early detection enables timely interventions before complications arise. Changes to your diet, increased physical activity, or stress reduction strategies may be essential. These proactive measures can help lower your blood pressure and enhance your quality of life.
By staying informed and taking proactive measures, you can safeguard your heart, brain, and kidneys. Managing high blood pressure is a lifelong commitment, yielding benefits such as improved health and greater peace of mind.
Exploring the Key Factors That Contribute to Hypertension: Understanding Its Origins
Numerous factors contribute to the emergence of high blood pressure, broadly categorised into genetic, lifestyle, and environmental influences. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role; individuals with a family history of hypertension are more likely to develop the condition themselves. This hereditary aspect implies that certain biological factors may predispose individuals to high blood pressure.
 Lifestyle choices also have a substantial impact on the risk of developing hypertension. Diets excessively high in sodium can lead to water retention, increasing blood volume and consequently raising blood pressure. On the other hand, diets rich in potassium can help alleviate blood pressure. Fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of potassium, which aids in counteracting the adverse effects of excessive sodium by promoting relaxation in blood vessel walls. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle increases the likelihood of hypertension. Long periods of inactivity often lead to weight gain, placing additional strain on the heart and arteries, ultimately elevating blood pressure over time.
Lifestyle choices also have a substantial impact on the risk of developing hypertension. Diets excessively high in sodium can lead to water retention, increasing blood volume and consequently raising blood pressure. On the other hand, diets rich in potassium can help alleviate blood pressure. Fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of potassium, which aids in counteracting the adverse effects of excessive sodium by promoting relaxation in blood vessel walls. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle increases the likelihood of hypertension. Long periods of inactivity often lead to weight gain, placing additional strain on the heart and arteries, ultimately elevating blood pressure over time.
Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking are also well-known contributors to hypertension. Heavy drinking can significantly raise blood pressure, with risks increasing in proportion to the amount consumed. Smoking damages the heart by harming blood vessel walls and reducing their elasticity. This loss of flexibility can lead to higher blood pressure levels. Moreover, stress and poor sleep patterns are recognised risk factors that can contribute to progressively rising blood pressure. Living in fast-paced urban environments often exacerbates these issues, compromising mental health and potentially intensifying hypertension.
Understanding these fundamental causes is critical for effectively managing and preventing high blood pressure. By adopting healthier lifestyle choices and staying aware of personal risk factors, individuals can significantly lower their likelihood of developing hypertension. Knowledge truly empowers individuals in the battle against this widespread condition.
Recognising Symptoms of Hypertension: Effective Diagnostic Approaches
High blood pressure is often dubbed “the silent killer” due to its lack of noticeable symptoms. Most people with hypertension will not observe any clear signs until significant damage has occurred. This absence of symptoms emphasises the necessity of regular monitoring. Without consistent checks, high blood pressure can go undetected, potentially leading to severe health issues, such as heart attacks or strokes.
Some individuals may experience infrequent symptoms, including headaches, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds, but these typically occur only when blood pressure reaches dangerously high levels. Since hypertension often lacks symptoms, healthcare professionals recommend regular blood pressure screenings. This is particularly essential for individuals over 40 or those with risk factors such as obesity, inactivity, or a family history of heart disease to have their blood pressure checked regularly.
Diagnosis involves measuring blood pressure with a sphygmomanometer in a clinical setting, comparing readings against established guidelines. Consistently elevated readings above 130/80 mmHg usually result in a diagnosis of hypertension. After diagnosis, further assessments may be necessary to rule out secondary causes of high blood pressure and evaluate overall cardiovascular health.
Recognising the significance of early diagnosis empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their high blood pressure. With the right knowledge and resources, those at risk can implement lifestyle changes or seek medical intervention to protect their long-term health.
Holistic Approaches to Effectively Manage High Blood Pressure
Successfully managing high blood pressure involves a holistic approach that combines lifestyle changes, potential medication, and ongoing monitoring. The good news is that many individuals can maintain healthy blood pressure levels through healthy habits alone. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, is vital for maintaining a healthy weight and enhancing cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week.
Diet plays a crucial role in successful blood pressure management. Adopting a balanced diet is fundamental for lowering blood pressure. The ideal diet should be low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium while being rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is a highly regarded option that focuses on foods promoting heart health and assisting in lowering blood pressure. Essential nutrients such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium contribute to its effectiveness.
Incorporating stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can significantly affect blood pressure levels. Chronic stress is acknowledged as a contributing factor to elevated readings, making relaxation techniques an indispensable component of a holistic approach to hypertension management. Individuals should also remain mindful of their consumption of alcohol and tobacco, both of which can exacerbate high blood pressure.
If lifestyle changes are insufficient, healthcare providers may suggest medications to help control hypertension. These can include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and more. Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential, as it enables individuals and their healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of management strategies and make necessary adjustments.
Taking a proactive approach to managing high blood pressure can lead to improved health outcomes and a reduced risk of complications. With the right strategies, individuals can take control of their cardiovascular health and enjoy fulfilling lives.
The Role of Dietary Supplements in Blood Pressure Management
Navigating the complexities of hypertension management often leads individuals to explore the potential benefits of dietary supplements. While supplements should not replace a healthy lifestyle or prescribed medications, they can be valuable adjuncts in blood pressure management when integrated into a holistic approach. Supplements can provide essential nutrients that support cardiovascular health, presenting an appealing option for those looking to enhance their overall well-being.
Certain supplements have gained attention for their potential to support healthy blood pressure levels. For instance, magnesium, potassium, and omega-3 fatty acids are frequently highlighted for their positive effects on heart health. These nutrients may aid in relaxing blood vessels, counteracting sodium’s effects, and reducing inflammation, respectively. However, it is crucial to approach supplementation with a clear understanding of its limitations.
While supplements can enhance overall health, they should not be viewed as a cure-all for hypertension. Relying solely on supplements without simultaneously adopting healthy lifestyle changes can result in missed opportunities for improving blood pressure management. Dietary modifications and regular exercise should form the foundation of any plan to manage high blood pressure. Supplements can be supportive but should complement—not replace—these core strategies.
Before embarking on any supplement regimen, consulting healthcare providers is essential. Each individual’s health needs are unique, and a healthcare professional can provide guidance on safe and appropriate options. Collaborating with healthcare providers helps individuals make informed supplement choices, ensuring that their selections align with their health goals, supporting better blood pressure control and minimising the risk of complications.
Examining the Role of Supplements in Effective High Blood Pressure Management
Supplements can significantly contribute to blood pressure management, particularly when integrated into a comprehensive dietary and lifestyle modification plan. Specific vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids have shown promise in promoting cardiovascular health and may assist in regulating blood pressure levels. For individuals managing hypertension, exploring appropriate supplements can be an empowering step towards improved health.
Utilising Magnesium for Relaxation and Blood Pressure Control
One of the most extensively studied supplements is magnesium. This essential mineral is renowned for its ability to help relax blood vessels, potentially leading to lower blood pressure levels. Research indicates that adequate magnesium intake can help maintain blood pressure within a healthy range, particularly for individuals already diagnosed with hypertension. Foods rich in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains, are important additions to any diet. However, many people struggle to obtain sufficient magnesium through food alone. In such cases, magnesium supplementation can be beneficial.
Potassium is another essential nutrient for regulating blood pressure. This mineral helps balance sodium levels, leading to lower overall blood pressure. Supplementation can be particularly advantageous for individuals who do not consume enough potassium-rich foods, such as bananas, avocados, and sweet potatoes. Maintaining an optimal potassium-to-sodium ratio is crucial for supporting healthy blood pressure levels, making potassium supplementation an appealing option for many.
Omega-3 fatty acids, sourced from fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Research has shown that omega-3 supplementation can lead to modest reductions in blood pressure, making it a valuable addition for individuals aiming to manage hypertension. The heart-healthy benefits of omega-3s extend beyond merely regulating blood pressure; they positively contribute to overall cardiovascular health and wellness.
Customised Approaches: Tailoring Supplement Strategies for Individual Needs
Supplements can support high blood pressure management when integrated with healthy lifestyle changes. Incorporating magnesium, potassium, and omega-3 fatty acids into your routine may enhance heart health. It is essential to align supplements with your individual health needs. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and efficacy.
Recognising the Limitations of Supplements in Hypertension Management
Despite their potential benefits, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of supplements in managing high blood pressure. While certain nutrients can bolster cardiovascular health, supplements should not be perceived as standalone solutions or substitutes for a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle choices. Over-reliance on supplements may lead to complacency regarding necessary lifestyle modifications required for effectively managing hypertension.
The quality, potency, and effectiveness of supplements can vary significantly, making it essential for consumers to choose reputable brands. Not all supplements are created equal; some may contain ingredients that interact with medications or may not be adequately absorbed by the body. Furthermore, excessive consumption of specific supplements can lead to adverse effects. For instance, high doses of potassium supplementation can induce hyperkalemia, a potentially dangerous condition for individuals with kidney issues.
Supplements Can Help—but They’re Not a Shortcut
The effectiveness of supplements can vary widely among individuals. Health conditions, genetics, and lifestyle factors all influence their efficacy. What benefits one person may not yield the same results for another. It is crucial to maintain realistic expectations: supplements are merely one aspect of a broader blood pressure management strategy. They do not replace lifestyle changes or medical care. Consider supplements as a helpful tool—not a standalone solution. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and prescribed medication may also be necessary components of an effective management plan.
Consult your healthcare provider before introducing any new supplements. This precaution helps you avoid harmful interactions or unnecessary risks. Your doctor can guide you towards options that align with your health needs. A well-rounded plan is most effective. Combining healthy habits with expert advice offers the most reliable method for controlling blood pressure, thereby supporting long-term heart health.
The Importance of Consulting Healthcare Providers Before Supplementation
Before initiating any supplement regimen, it is vital to engage in discussions with healthcare providers. Each individual’s health profile is unique, meaning dietary requirements and potential interactions with medications can vary significantly. A healthcare provider can thoroughly evaluate your health status and offer tailored recommendations, ensuring that any supplementation strategy aligns with overall health goals.
Consultation with healthcare professionals is particularly critical for those already managing chronic conditions or taking medications for hypertension. Certain supplements may interact with prescribed blood pressure medications, potentially leading to adverse effects or reduced treatment efficacy. For example, potassium supplements may pose complications for individuals on specific antihypertensive medications, underscoring the necessity for professional guidance before introducing new supplements.
Understanding the potential risks and benefits of supplementation is vital. Not all supplements undergo the same level of scrutiny as prescription medications, which can lead to variability in quality and potency. Healthcare providers can recommend high-quality products and help identify reputable brands that undergo third-party testing for safety and efficacy.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that individuals maintain open lines of communication regarding their health status and any changes in their supplement regimen. This ongoing relationship allows for necessary adjustments based on blood pressure readings and overall health progress. An informed approach to supplementation, guided by healthcare expertise, can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their blood pressure and enhancing overall health outcomes.
Highly Effective Supplements for Supporting High Blood Pressure Management

Several supplements have gained recognition for their potential efficacy in effectively managing high blood pressure. Among these, magnesium, potassium, and omega-3 fatty acids stand out due to their well-documented benefits for cardiovascular health. Understanding the roles of these supplements can empower individuals to make informed decisions in their hypertension management strategies.
Magnesium: The Mineral That Promotes Blood Vessel Relaxation
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in numerous biochemical processes within the body. It plays a crucial role in muscle and nerve function, energy production, and maintaining normal blood pressure. Research indicates that magnesium supplementation can significantly lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension, particularly among those with low dietary intake. Foods rich in magnesium, such as spinach, almonds, and black beans, are excellent choices; however, many individuals require supplements to meet their daily magnesium needs.
Potassium: Balancing Sodium and Supporting Heart Health
Potassium is another vital nutrient that regulates blood pressure. By counteracting sodium’s effects, potassium helps to relax blood vessel walls and decrease blood pressure. High-potassium foods, such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens, are excellent choices for those seeking to manage hypertension. Supplementation can be beneficial for individuals who may not consume sufficient potassium through their diet, but it must be approached with caution, particularly for those with kidney issues.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Anti-Inflammatory Allies for Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily derived from fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel, have been extensively researched for their cardiovascular benefits. These healthy fats reduce inflammation and improve endothelial function, thereby lowering blood pressure. Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids has shown promise in modestly decreasing blood pressure levels, making them a valuable addition to a heart-healthy lifestyle. Fish oil or algal oil supplements can provide a convenient alternative for individuals who do not regularly consume fish. Incorporating these popular supplements into a broader strategy that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise can help individuals manage their blood pressure effectively. However, it is crucial to approach supplementation mindfully and consult with healthcare professionals to ensure safety and efficacy.
Investigating the Role of Coenzyme Q10 in Blood Pressure Management
Coenzyme Q10, often abbreviated as CoQ10, is a potent antioxidant that plays a crucial role in cellular energy production. This compound has garnered attention for its potential benefits in lowering blood pressure, making it an appealing option for individuals seeking to manage hypertension. Exploring the benefits, dosage recommendations, and evidence supporting CoQ10’s role in blood pressure management can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Investigating CoQ10’s Benefits for Blood Pressure Control
CoQ10 is essential for the proper functioning of cells, particularly in the heart and blood vessels. Its antioxidant properties help reduce oxidative stress, which can damage blood vessels and contribute to elevated blood pressure levels. CoQ10 may assist in lowering blood pressure in individuals with hypertension by improving endothelial function and blood flow.
Research indicates that CoQ10 supplementation can lead to modest reductions in blood pressure, particularly among individuals diagnosed with hypertension. Some studies have reported reductions of 10-17 mmHg in systolic blood pressure and 5-10 mmHg in diastolic blood pressure among those taking CoQ10 supplements. These findings suggest that CoQ10 could be a valuable addition to a comprehensive hypertension management plan.
Additionally, CoQ10 may offer benefits beyond its effects on blood pressure. Its role in promoting heart health and improving energy production can enhance overall well-being. Individuals with cardiovascular disease or those taking statin medications, which can deplete CoQ10 levels, may particularly benefit from supplementation.
Incorporating CoQ10 into a holistic approach to managing hypertension can provide individuals with a natural option for supporting cardiovascular health. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before supplementation, as individual needs vary significantly.
Optimal Dosage and Safety Considerations for CoQ10
When considering CoQ10 supplementation, determining the appropriate dosage is vital for maximising its benefits while minimising potential side effects. Typical doses of CoQ10 range from 100 to 200 mg per day, although some studies have employed higher doses with positive outcomes. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to establish the optimal dosage based on individual health profiles and goals.
CoQ10 is generally regarded as safe for most individuals, with few reported side effects. Some may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, or dizziness, but these effects are typically transient. Individuals taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, should consult their healthcare provider before commencing CoQ10, as it may interact with these medications.
Monitoring the effects of CoQ10 supplementation is crucial, especially for individuals managing hypertension. Regular blood pressure checks can help assess the supplement’s effectiveness and guide any necessary dosage adjustments. By collaborating closely with healthcare providers, individuals can ensure their CoQ10 regimen is safe and effective.
Incorporating CoQ10 into a comprehensive hypertension management strategy can promote cardiovascular health and support overall well-being. With careful attention to dosage and safety, CoQ10 may offer a valuable addition to the toolkit for managing high blood pressure.
Research Findings: Evidence Supporting CoQ10 and Blood Pressure
The research surrounding CoQ10 and its role in blood pressure management is promising, although further studies are needed to establish definitive conclusions. Various clinical trials have investigated the effects of CoQ10 supplementation on blood pressure levels, with many reporting positive outcomes. For instance, a meta-analysis of multiple studies found that CoQ10 supplementation led to significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure among individuals with hypertension.
While the findings are encouraging, it is crucial to recognise the variability in individual responses to CoQ10 supplementation. Some individuals may experience more pronounced reductions in blood pressure than others, depending on factors such as baseline levels, overall health, and adherence to a comprehensive management plan. Additionally, the duration of supplementation and the specific formulations used can influence results.
As interest in complementary therapies expands, ongoing research into CoQ10’s long-term effects on blood pressure and cardiovascular health will be essential. Individuals contemplating CoQ10 should remain informed about emerging findings and consult their healthcare providers for guidance on the most effective strategies for managing their hypertension.
CoQ10 presents a promising option for those seeking natural ways to manage high blood pressure and enhance cardiovascular health. By understanding the benefits, dosage considerations, and current evidence, individuals can make informed decisions about integrating CoQ10 into their health regimen.
Garlic: A Natural Ally for Managing Blood Pressure
Garlic, a commonly used culinary ingredient, has long been celebrated for its potential health benefits, particularly concerning cardiovascular health. Research suggests that garlic may significantly lower blood pressure, making it an attractive option for individuals seeking natural solutions for hypertension management. Understanding the mechanisms behind garlic’s effects, the various forms and dosages available, and the clinical evidence supporting its use can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
How Garlic Works: Mechanisms Behind Its Benefits
Garlic contains an active compound known as allicin, responsible for many of its health-promoting properties. Allicin has been shown to exert a vasodilatory effect, meaning it helps relax blood vessels and enhance blood flow. This relaxation of blood vessels can lead to lower blood pressure levels, making garlic a valuable addition to the diet for those managing hypertension.
In addition to its vasodilatory effects, garlic may possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which can further contribute to cardiovascular health. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation within the body, garlic may help protect against damage that can lead to elevated blood pressure levels.
Numerous studies have investigated the effects of garlic on blood pressure, with many reports indicating positive outcomes. Research suggests that regular garlic consumption may lead to modest reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, particularly in individuals with hypertension. These findings highlight garlic’s potential as a natural remedy for managing high blood pressure.
Incorporating garlic into a heart-healthy diet can provide numerous benefits beyond blood pressure management. As a versatile ingredient, it can enhance the flavour of various dishes while promoting overall health. For those seeking natural alternatives to pharmaceuticals, garlic may be a valuable addition to their dietary regimen.
Forms and Dosages of Garlic: Making Informed Choices
 Garlic supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and extracts. Each form may exhibit different bioavailability, affecting how well the body absorbs and utilises the active compounds. Aged garlic extract, in particular, has gained popularity due to its high concentration of beneficial compounds and is often used for its potential health benefits.
Garlic supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and extracts. Each form may exhibit different bioavailability, affecting how well the body absorbs and utilises the active compounds. Aged garlic extract, in particular, has gained popularity due to its high concentration of beneficial compounds and is often used for its potential health benefits.
The appropriate dosage of garlic for blood pressure management can vary based on the form used and the concentration of active ingredients. Generally, studies have employed doses ranging from 600 to 1,200 mg of garlic extract daily, while whole garlic cloves may require higher quantities to achieve similar effects. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to determining the most suitable dosage tailored to individual health needs and goals. While garlic is generally considered safe for most individuals, it may lead to side effects such as bad breath or gastrointestinal discomfort. Garlic can interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners, so it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before supplementing.
Incorporating garlic into one’s diet, whether through whole cloves or supplements, can support heart health and aid in blood pressure management. By understanding the various forms and dosages available, individuals can make informed choices about how best to integrate this potent ingredient into their health regimen.
Clinical Studies: Evidence Supporting Garlic’s Efficacy
A growing body of research supports the potential benefits of garlic for lowering blood pressure. Numerous clinical studies have investigated the effects of garlic supplementation on individuals with hypertension, with many reporting significant results. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the journal Hypertension found that garlic supplementation led to notable reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure among participants, particularly those with higher baseline levels.
While the results are promising, it is crucial to recognise that individual responses to garlic supplementation can vary widely. Some studies have shown more substantial blood pressure reductions, while others have reported minimal effects. Factors such as dosage, duration of supplementation, and individual health profiles can influence the outcomes of these studies.
The type of garlic used in supplementation can also impact results. Aged garlic extracts have been shown to possess higher bioavailability and may be more effective than fresh garlic or other forms. As research continues to explore the relationship between garlic and blood pressure management, individuals should remain informed about emerging findings and consult healthcare providers for guidance.
Incorporating garlic into a heart-healthy diet can provide numerous benefits, particularly for those managing high blood pressure. With the potential to support cardiovascular health, garlic is a natural option for individuals seeking alternatives to pharmaceutical interventions.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions Associated with Garlic
While garlic is generally safe for most individuals, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects and medication interactions. Common side effects of garlic supplementation include gastrointestinal discomfort, heartburn, and bad breath. These effects can often be mitigated by taking garlic supplements with food or opting for enteric-coated formulations.
Garlic can also interact with certain medications, particularly anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs. This interaction may elevate the risk of bleeding, making it vital for individuals taking these medications to consult with a healthcare provider before starting garlic supplementation. Garlic may also affect the metabolism of certain drugs, altering their efficacy.
For individuals with specific health conditions, such as bleeding disorders or gastrointestinal issues, caution is advised when considering garlic supplementation. Consulting with a healthcare provider can provide valuable insights into potential risks and help determine whether garlic suits blood pressure management.
In summary, while garlic offers numerous health benefits, individuals should approach supplementation mindfully, considering potential side effects and interactions. By consulting healthcare professionals, individuals can safely incorporate garlic into their hypertension management strategies and enjoy its cardiovascular benefits.
Understanding the Connection Between Vitamin D and Hypertension
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” plays an essential role in overall health, including its potential impact on blood pressure regulation. Emerging research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to hypertension, making it vital for individuals to understand the role of this crucial nutrient in managing blood pressure. By exploring the relationship between vitamin D and hypertension, individuals can proactively support their cardiovascular health.
Understanding Vitamin D’s Contribution to Blood Pressure Regulation
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin sourced through sunlight exposure, dietary intake, and supplements. It is essential for maintaining healthy bones and teeth, enhancing immune function, and regulating various bodily processes. Recent studies have examined the link between vitamin D levels and hypertension, suggesting that adequate vitamin D may play a role in sustaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Research indicates that individuals with low vitamin D levels are more prone to hypertension. The precise mechanisms underlying this relationship are still being investigated. However, it is believed that vitamin D may influence blood pressure through its effects on calcium metabolism, inflammation, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which is a key regulator of blood pressure.
While the evidence linking vitamin D deficiency to hypertension is compelling, it is crucial to recognise that not all individuals with low vitamin D levels will develop high blood pressure. However, ensuring adequate vitamin D intake may benefit those looking to support their cardiovascular health and manage hypertension more effectively. Incorporating vitamin D-rich foods into the diet, engaging in safe sun exposure, and considering supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare provider can help individuals achieve optimal vitamin D levels and potentially enhance blood pressure management.
Determining the Optimal Dosage of Vitamin D for Blood Pressure Control
Finding the appropriate dose of vitamin D for blood pressure control depends on individual health needs and current vitamin D levels. For most adults, the recommended amount is 600 to 800 IU per day. Some individuals may require higher amounts to achieve healthy blood levels. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the best dose for your specific situation.
Various factors affect vitamin D requirements, including age, body weight, geographical location, and daily habits. Individuals living in areas with limited sunlight exposure are at a higher risk of deficiency. These individuals may benefit from taking a supplement. A healthcare provider can assess your needs and recommend a dose that fits your health profile.
It is crucial to note that excessive vitamin D intake can lead to toxicity, resulting in elevated calcium levels and potential health complications. Hence, monitoring vitamin D levels through blood tests and collaborating with healthcare professionals is essential to ensure safety and efficacy. Individuals can take proactive steps to support their cardiovascular health and potentially reduce their risk of hypertension by focusing on achieving optimal vitamin D levels. Finding the right balance is key to reaping the benefits of this essential nutrient.
Exploring Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
Vitamin D can be obtained from various dietary sources, making it accessible for individuals seeking to boost their intake. Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are excellent sources of vitamin D. Additionally, fortified foods, including dairy products, plant-based milk alternatives, and breakfast cereals, can provide significant amounts of this vital nutrient.
Sunlight exposure is another natural method to obtain vitamin D. When sunlight interacts with the skin, the body synthesises vitamin D. This makes outdoor time particularly important, especially during sunny months. However, several factors can limit vitamin D production, including geographical location, skin pigmentation, and sunscreen usage. Consequently, some individuals may need to obtain vitamin D from food or supplements instead.
Supplements can be an effective solution for those unable to secure sufficient vitamin D through dietary means or sunlight exposure. Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is generally regarded as the most effective form for increasing blood levels of vitamin D. When selecting supplements, opting for reputable brands that undergo third-party testing can assure quality and safety.
Using a combination of dietary sources, sunlight exposure, and supplementation can help individuals achieve and maintain optimal vitamin D levels. This proactive approach may support overall health and potentially contribute to improved blood pressure management.
Clinical Studies on Vitamin D and Hypertension
Researchers have reviewed numerous studies regarding vitamin D supplements and blood pressure. They found a slight decrease in pressure for some groups. Individuals with diabetes, low vitamin D levels, or short supplementation periods (under 20 weeks) experienced the best outcomes. In these cases, both systolic and diastolic blood pressure exhibited slight reductions. Nevertheless, not everyone benefitted; individuals with healthy vitamin D levels or those on long-term supplementation showed minimal or no changes.
The results from research on vitamin D and blood pressure indicate promising trends, but not all studies demonstrate a clear connection. Variations in study designs, dosage used, and participant characteristics may elucidate these mixed results. As research progresses, it remains crucial to stay updated. New findings may redefine the role of vitamin D in managing high blood pressure. Consulting a healthcare provider can help you determine if and how to incorporate it into your health strategy. Vitamin D supports many aspects of overall health and may also aid in blood pressure regulation. Ensuring adequate intake through dietary sources, safe sun exposure, or supplementation can positively impact overall well-being and heart health.
Common Questions Regarding Blood Pressure Management
Which supplements are most effective for managing high blood pressure?
Some of the most effective supplements for controlling high blood pressure include magnesium, potassium, omega-3 fatty acids, and Coenzyme Q10. These nutrients can support cardiovascular health and contribute to better blood pressure regulation.
How does magnesium contribute to lower blood pressure?
Magnesium helps to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, leading to reduced blood pressure levels. Adequate magnesium intake is associated with a lower risk of hypertension.
What is potassium’s role in regulating blood pressure?
Potassium helps counteract the effects of sodium in the body, promoting relaxation of blood vessel walls and lowering blood pressure. A diet rich in potassium can greatly benefit individuals with hypertension.
Are there risks associated with using supplements for high blood pressure?
Yes, certain supplements can interact with medications or cause side effects. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before beginning any supplementation to ensure safety and effectiveness.
What is the recommended dosage of omega-3 fatty acids for blood pressure control?
Typical dosages of omega-3 supplements range from 1,000 to 4,000 mg per day. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable dosage tailored to individual needs.
Can garlic supplements effectively lower blood pressure?
Yes, garlic supplements, particularly those containing aged garlic extract, have shown potential benefits for lowering blood pressure due to their active compound, allicin. How does Coenzyme Q10 contribute to blood pressure management?
Coenzyme Q10 is an antioxidant that may help lower blood pressure by enhancing endothelial function and reducing oxidative stress within the body.
What is the recommended daily intake of vitamin D?
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin D in adults is 600 to 800 IU per day. However, individual requirements may vary, so it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for personalised recommendations.
Can lifestyle changes alone effectively manage high blood pressure?
For many individuals, lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can effectively control high blood pressure without the need for medication. However, some individuals may still require medication for optimal management.
Is it safe to take multiple supplements for blood pressure management?
Taking multiple supplements can be safe, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to ensure there are no interactions and that the combination is suitable for individual health needs.
Connect with us on Facebook!
The Article: Essential Supplements for Managing High Blood Pressure appeared first on https://janestevensnutrition.com
The Article: Essential Supplements for High Blood Pressure Management appeared first on https://janestevens.net
The Article High Blood Pressure Management with Essential Supplements Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com

